According to the power supply mode, the power system of the observation level underwater vehicle can be divided into two types: cable power supply and battery power supply. Most small ROVs use cable power supply. ROV itself literally means remote control. Therefore, it does not mean that a cable is an ROV and a cylindrical one without cable is an AUV. For deeper application scenarios, This distinction can also be said to be correct, because the cable provides signal transmission in addition to power supply. At present, deep water has no way to carry out high-capacity wireless communication. However, we should know that the essential difference between ROV and AUV is whether they have autonomy. At present, almost all observation level ROVs on the market are powered by cables. In addition to convenience, no one wants to see their beloved “baby” swim and disappear
We will not introduce the hydraulically driven ROV in this article. However, the size of the hydraulically driven light work level remote control robot is also shrinking. If the observation level ROV wants to be equipped with some underwater tools, the hydraulic system is a good choice, because the power density is much higher under the same volume.
1.Mooring power supply
The power system of underwater vehicle has a very small market share in the electrical industry. Therefore, many aspects of ROV electrical system, including development, are transferred from other fields, and the principle is the same. Many body instruments and equipment on the underwater vehicle use low-voltage DC power supply, but if low-voltage DC is used to supply power from the water surface to the underwater, the mooring must use a very thick conductor. Therefore, the AC transmission with step-up transformer on the surface and step-down transformer under the water is helpful to reduce the wire section of umbilical cable. The size and weight of conventional 50 / 60Hz transformer are large. Many ROV designs use high-frequency AC system. For a given power, high-frequency significantly reduces the size and weight. With the development and popularization of DC converter, DC can also increase and decrease voltage. ROV power system has now realized high-voltage DC transmission.
According to the type of underwater vehicle and the length of umbilical cable, the power system can be AC or DC. Generally speaking, the work level remote control underwater robot adopts AC to convert part of the power underwater into DC. In this transmission process, there will usually be more than 20% power loss. If the tether is long and the power is large, the AC umbilical is used. In addition, due to the large size of the work level robot, it can accommodate high-power electrical equipment and transmit power underwater through high voltage, which can reduce loss. For example, some 6000 meter depth robots use 460hz, 6.6 kV.
Leopard ROV of Saab seaeye is powered by 3000 VAC with high frequency transmission of 800Hz
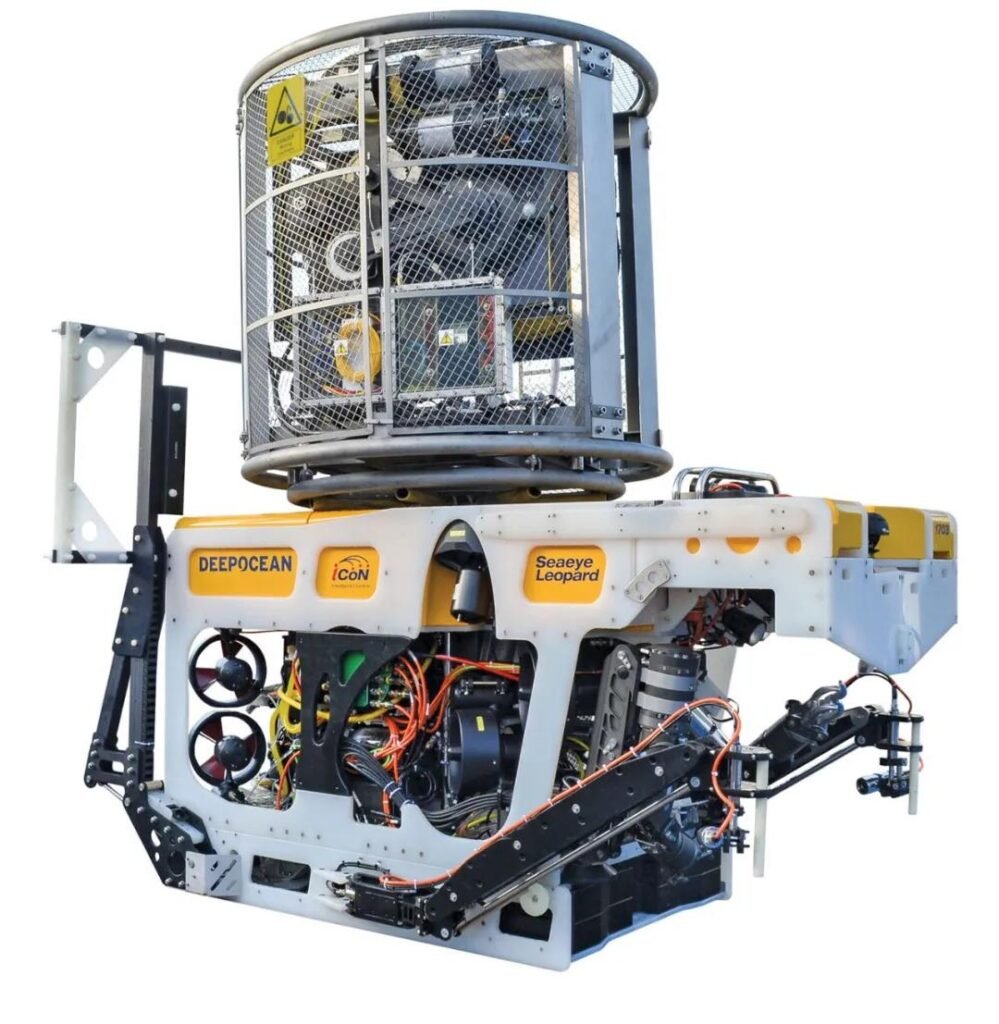

High frequency AC is used because the size and weight of underwater transformer equipment can be reduced. It has been calculated that the transformer mass can be reduced by 66% by increasing the frequency from 60Hz to 400Hz. Leopard ROV of Saab seaeye transmits 3000 V AC at a high frequency of 800Hz, which greatly reduces the size of underwater transformer and the diameter of umbilical cable.
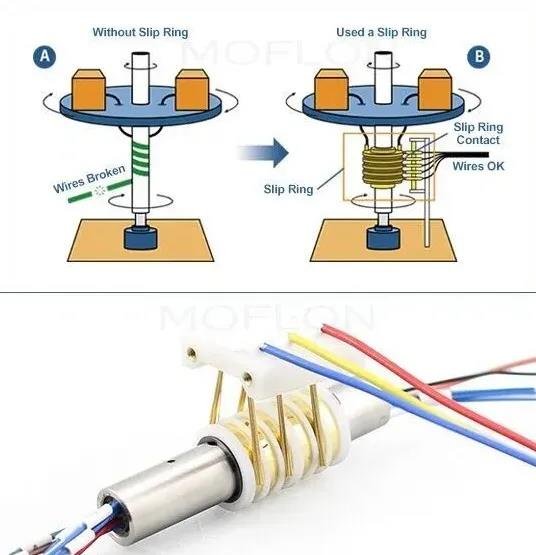
If the mooring line is long, a cable winch with slip rings is required. Slip ring, also known as rotary joint, is an optical / electromechanical joint through which photoelectric signals and power can be transmitted. The equipment is very important for continuous power supply and remote control of the underwater robot during winch rotation. If the umbilical cable is only copper wire, the slip ring is a simple structure composed of brush and rotating metal ring. However, if there is optical fiber in the umbilical, the slip ring will be very complex and expensive. Some companies provide photoelectric slip rings, such as Moog and trolex, which can be transmitted in multiple channels, both electrically and optically. The design structure and working principle of single-channel optical fiber slip ring are very different from that of multi-channel optical fiber slip ring. Multi channel optical fiber slip ring only has multi-mode transmission, while single-channel optical fiber slip ring can have single-mode and multi-mode. Each slip ring has a fixed number of channels. How many semaphores you need to use this slip ring to transmit is also a matter that has been done before the equipment design. These should be selected. Even for the needs of final expansion, two standby channels can be reserved. Although they are not available now, they can also be used later if the equipment is upgraded or updated. In many cases, the selection of slip ring and the number of fiber cores have to be designed with redundancy in case of accident.
Principle of slip ring. If there is no slip ring, the cable will be wound on the winch with rotation
For the larger AUV system, due to the large size of the body and umbilical winch, it is necessary to customize the retraction and retraction system (LARS) and umbilical management system (umbilical repeater TMS). Although not many small observation robots use AC, it doesn’t mean there is No. A robot developed by the underwater System Technology Laboratory of the University of Porto is converted underwater into 375 V DC through 230 V AC, and then further converted into 48 V DC to drive the propeller. Mixed optical fiber is very common in AC umbilical, but AC will interfere with the signal and need some shielding.
DC is more common for observation level ROV for the following reasons:
Size limit
cost
Applicable water depth / umbilical length
Power requirements
Complexity
However, with the increase of the power demand of the robot itself, the voltage transmitted along the umbilical cable must also increase. Someone has developed a medium-sized observation grade ROV (90kg) with 150V DC power supply. Some commercial manufacturers have also developed underwater robots powered by 150-300 V DC.
In recent years, the trend is to convert 230 V AC into 400-500 V DC medium voltage on the water surface, and then deliver it to underwater robots. This method has been applied in many ocean observation stations. The voltage transmitted to the main node is kV, and then transmitted to the auxiliary node with 400 V DC, and then the 400 V DC is converted into the working voltage of electronic equipment and sensors, such as 48 V, 24 V, 12 V and so on. Many observation level underwater robots directly use 400-500 V DC, such as seatronics and Saab seaeye.
The advantage of using mooring power supply / information transmission is that it is not limited by power and data processing capacity, and reduces the volume and weight of the robot body. But there are also disadvantages. When the robot becomes a little larger, it needs additional manpower and mechanical equipment, and the operation and operation cost of the system will rise.
- Battery powered
The battery power supply system is used more on AUV (autonomous underwater vehicle), but less on ROV (remote controlled underwater vehicle). However, for observation ROV, the battery can replace the mooring cable for power supply. Batteries can be divided into two categories:
Primary battery
Once the battery is discharged, it cannot be recharged. The most common is alkaline batteries. Their capacity density is about 140wh · kg-1. They are cheap and safe. However, when stored for a long time, they will release hydrogen. The energy density of lithium primary battery has reached 460-600 wh · kg-1, which is 6-7 times that of lead-acid battery, but the ordinary 300wh · kg-1 is already very high. Lithium batteries are very expensive and must be used with special care. Some models are easy to explode, so they are not commonly used in today’s underwater robots.
Secondary battery
The battery can be charged and discharged for many times and has a long service life. This type of battery is widely used in underwater vehicles. Some ROVs and hybrid ROVs use this type of battery. According to different chemical reactions, there are lead-acid batteries, silver zinc batteries, nickel cadmium batteries and lithium-ion batteries. Lead acid batteries are simple and cheap, but they are stupid and heavy; Silver zinc battery has high energy density, but it is expensive and short service life, about 100-250 cycles; Nickel cadmium battery is very suitable for high current applications. It is not expensive, but it is also heavy; Lithium ion batteries are small and have higher energy density than other batteries, but they are the most expensive. Care must be taken to prevent combustion and explosion.
For some special underwater robots, such as ice robots, ships cannot follow. They must drag extremely long cables, even tens of kilometers long. In this case, it is obvious that cable power supply is difficult to achieve, so they have to be driven by batteries.
Another advantage of battery driven ROV is that in high-risk application scenarios, such as the mooring cable of underwater robot is accidentally entangled, it can be cut off and then return to the predetermined area for recycling under signal command. Cameron’s film “ghost of the abyss” has the picture of ROV cutting off the optical fiber《Deep sea ghost 》movie ROV and sister submersible

Micro observation ROV is usually powered by battery. The thin umbilical cable and the small size of ROV reduce the water resistance and prolong the underwater working time.
Aquabotix Endura also supports AC power supply.
The main disadvantage of battery power supply is battery life, which is related to the energy density, capacity and life of the battery. To overcome this defect, underwater wireless charging may be a good scheme. Saab, oceaneering, Saipan, together with Statoil, shell, BP and other companies have developed underwater charging schemes.
Murcia, Spain, has developed an underwater robot that uses solar energy to charge. The underwater robot is connected to a small unmanned platform (battery panel) through a tether. When the ROV sails, it can lead the surface battery panel forward together. This method can not only supplement power and help navigation, but also carry out wireless remote communication and control, but the disadvantage is that the action of ROV will be constrained by the resistance of floating objects and inconvenient to move.
There are also some “strange” charging methods. Someone has invented a device for generating power by using phase change energy storage materials under the ocean temperature gradient. Of course, this novel method can also be combined with wireless charging. In short, there are countless combinations of charging and power generation. In order to improve durability, fuel cells can also be used, but underwater applications need a lot of research. At present, a few underwater robot prototypes using fuel cells have been developed. Underwater vehicles are becoming more and more intelligent, and the technology of sensors is developing faster and faster. With the increase of functions, the power demand will increase. The trend shows that the underwater robot needs higher power to cope with more complex working conditions and more accurate control, especially the working level ROV. Even the underwater resident ROV developed now, it is best to tie a cable to the underwater power supply, preferably hybrid power. There is also a demand for pure battery driven robots, not just some consumer grade ones. In special operation environment, battery driven robots are more suitable than tether driven robots.

